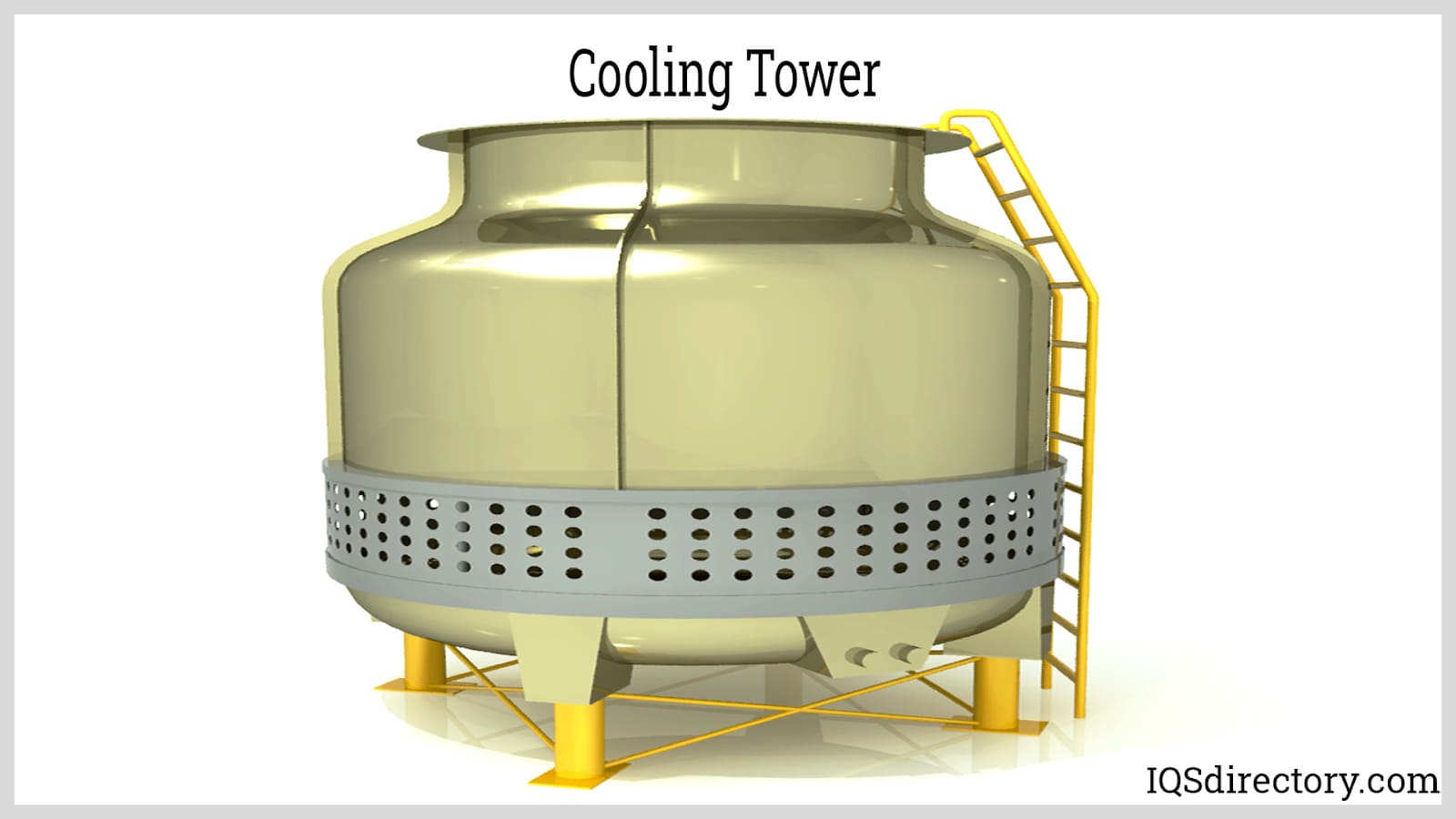
Cooling towers, also known as heat rejection devices, are systems that remove heat from fluids like water, in order to provide cool fluids to controlled environments. Cooling towers are typically used to cool down water or other fluids that have been heated during an industrial manufacturing process or some similar process. Read More…
Our circular FRP (fiberglass reinforced polyester) cooling towers are second to none. With five different models in production- one to meet every need for businesses of all sizes. We are the oldest, full-service fiberglass water cooling tower manufacturer in business today. We bring only the highest quality of customer service to our valued clients. When it comes to FRP cooling towers we bring...
At Delta Cooling Towers, Inc., we specialize in providing high-performance cooling solutions for a wide range of industries. Our innovative cooling towers are engineered to deliver optimal efficiency, durability, and reliability, ensuring that our clients experience effective temperature regulation in their operations.

At SPX Cooling Technologies, we specialize in providing innovative solutions for heat transfer needs through our wide range of high-performance cooling towers. We design, manufacture, and deliver custom-engineered systems that are built to meet the unique requirements of various industrial and commercial applications.

At Cold Shot Chillers, we create a number of chilling systems, including cooling towers. Our products are designed for durability and cost effectiveness. Our engineers can easily custom build any machine to fit the needs of a particular application.

More Cooling Tower Manufacturers
Cooling towers, also called heat rejection devices, are systems designed to remove heat from fluids, such as water, providing cooled fluids to controlled environments. They are commonly used to cool down water or other fluids that have been heated during industrial manufacturing or similar processes.
Application of Cooling Towers: Enhancing Efficiency Across Industries
Cooling towers are essential heat rejection devices used to transfer waste heat from industrial processes or HVAC systems into the atmosphere. They play a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for equipment, ensuring efficiency, safety, and longevity. By dissipating heat through the evaporation of water, cooling towers are widely applied across various industries, from power generation to manufacturing and commercial buildings. This article explores the key applications of cooling towers, their benefits, and how they support diverse sectors.
What Are Cooling Towers?
Cooling towers are specialized heat exchangers that remove excess heat from a system by cooling a water stream through evaporation. Hot water from industrial processes or air conditioning systems is circulated through the tower, where it is exposed to air. As the water evaporates, it releases heat into the atmosphere, cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated back to the system. Cooling towers are available in various types, including open-circuit, closed-circuit, and hybrid towers, each suited to specific applications based on factors like heat load, water quality, and environmental conditions.
Key Applications of Cooling Towers
Cooling towers are versatile systems with applications across a wide range of industries. Below are some of the primary uses:
-
- Power Generation
Cooling towers are integral to power plants, including thermal, nuclear, and combined-cycle facilities, where they manage the heat generated during electricity production.
-
- Steam Condensation: In thermal power plants, steam turbines generate electricity by driving generators. After the steam passes through the turbine, it must be condensed back into water to maintain the cycle. Cooling towers provide the necessary cooling to condense the steam, ensuring efficient operation.
- Heat Dissipation: Power plants produce significant amounts of waste heat. Cooling towers dissipate this heat into the atmosphere, preventing overheating of critical components like turbines and generators.
- Benefits: They improve energy efficiency, reduce water consumption through recirculation, and ensure consistent power output by maintaining optimal temperatures.
-
- Industrial Manufacturing
Manufacturing processes often generate substantial heat, requiring cooling towers to maintain equipment performance and product quality. Industries like steel, chemical, and petrochemical production rely heavily on cooling towers.
-
- Steel Production: In steel mills, cooling towers are used to cool furnaces, rolling mills, and other equipment that operate at high temperatures. They help maintain the structural integrity of machinery and ensure consistent production quality.
- Chemical Processing: Chemical reactions often produce exothermic (heat-releasing) reactions. Cooling towers remove this heat to prevent equipment damage and maintain safe operating conditions.
- Petrochemical Refineries: Refineries use cooling towers to manage heat from distillation, cracking, and other processes, ensuring efficient production of fuels and chemicals.
- Benefits: Cooling towers enhance equipment longevity, reduce downtime, and support high-volume production by maintaining stable temperatures.
-
- HVAC Systems for Commercial and Residential Buildings
Cooling towers are a key component of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems in large commercial buildings, hospitals, data centers, and residential complexes.
-
- Air Conditioning: In large buildings, chillers remove heat from indoor air to provide cooling. Cooling towers then dissipate the heat absorbed by the chiller, completing the cooling cycle.
- Data Centers: Data centers generate significant heat from servers and IT equipment. Cooling towers ensure these systems remain at optimal temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Hospitals and Schools: Cooling towers support HVAC systems in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, which is critical for patient care, student learning, and overall occupant well-being.
- Benefits: They reduce energy costs by improving HVAC efficiency, ensure occupant comfort, and protect sensitive equipment like servers from heat-related failures.
-
- Food and Beverage Processing
The food and beverage industry relies on cooling towers to maintain strict temperature control during production, ensuring product safety and quality.
-
- Pasteurization and Sterilization: Processes like pasteurization (e.g., for milk or juice) require precise temperature control. Cooling towers help cool equipment and products after heating, preventing spoilage.
- Refrigeration Systems: Cooling towers support refrigeration systems used in food storage, ensuring perishable goods like meat, dairy, and vegetables remain fresh.
- Breweries and Distilleries: In beverage production, cooling towers manage heat generated during fermentation and distillation, maintaining optimal conditions for yeast activity and product consistency.
- Benefits: They ensure compliance with food safety standards, prevent bacterial growth by maintaining low temperatures, and improve production efficiency.
-
- Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector uses cooling towers to manage heat in refining, processing, and production operations.
-
- Refinery Cooling: Cooling towers dissipate heat from processes like crude oil distillation, catalytic cracking, and reforming, ensuring safe and efficient production of gasoline, diesel, and other products.
- Gas Processing: In natural gas processing plants, cooling towers help cool compressors and other equipment, maintaining operational efficiency.
- Offshore Platforms: Cooling towers are used on offshore rigs to manage heat from drilling and power generation equipment, often in compact, corrosion-resistant designs to withstand harsh marine environments.
- Benefits: They enhance safety by preventing overheating, improve equipment reliability, and support continuous production in demanding conditions.
-
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In the pharmaceutical industry, cooling towers are critical for maintaining precise temperature control during drug production.
-
- Process Cooling: Many pharmaceutical processes, such as chemical synthesis and fermentation, generate heat. Cooling towers remove this heat to ensure consistent reaction conditions and product quality.
- Cleanroom HVAC: Cooling towers support HVAC systems in cleanrooms, where temperature and humidity control are essential to prevent contamination of drugs and medical devices.
- Benefits: They ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards, protect product integrity, and maintain sterile environments.
-
- Pulp and Paper Industry
The pulp and paper industry generates significant heat during processes like pulping, bleaching, and drying, making cooling towers indispensable.
-
- Equipment Cooling: Cooling towers manage heat from boilers, digesters, and drying machines, preventing equipment damage and ensuring smooth operation.
- Water Recirculation: They cool process water for reuse, reducing water consumption and supporting sustainable practices.
- Benefits: Cooling towers improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, and support high-volume production in paper mills.
-
- Plastic and Rubber Manufacturing
In plastic and rubber manufacturing, cooling towers are used to manage heat during molding, extrusion, and curing processes.
-
- Injection Molding: Cooling towers cool molds after plastic injection, ensuring rapid solidification and maintaining production speed.
- Rubber Curing: In rubber production, cooling towers manage heat from curing processes, ensuring consistent material properties.
- Benefits: They enhance production speed, improve product quality, and reduce energy costs by optimizing cooling efficiency.
Benefits of Cooling Towers Across Applications
Cooling towers offer several advantages that make them indispensable in various industries:
-
- Energy Efficiency: By using evaporative cooling, they reduce the energy required for heat rejection compared to air-cooled systems.
- Water Conservation: Many cooling towers recirculate water, minimizing consumption and supporting sustainable operations.
- Equipment Protection: They prevent overheating, extending the lifespan of machinery and reducing maintenance costs.
- Versatility: Cooling towers can be tailored to specific heat loads, environmental conditions, and space constraints, making them suitable for diverse applications.
- Cost Savings: Efficient heat management reduces energy costs and prevents costly downtime due to equipment failures.
Factors to Consider When Using Cooling Towers
While cooling towers are highly effective, their application requires careful consideration of several factors:
-
- Water Quality: Poor water quality can lead to scaling, corrosion, or biological growth (e.g., Legionella bacteria). Regular water treatment and maintenance are essential.
- Environmental Impact: Cooling towers release water vapor and may contribute to local humidity. In water-scarce regions, dry cooling towers or hybrid systems may be preferred.
- Noise Levels: Cooling towers can be noisy due to fans and water flow. Noise reduction measures, such as sound barriers or low-noise fans, may be necessary in urban settings.
- Space Requirements: Large cooling towers require significant space, which may be a constraint in compact facilities. Compact or modular designs can address this issue.
History
The concept of tower cooling has been utilized since ancient times. Civilizations such as those in Rome, Greece, the Middle East, and the Americas used water to evaporate heat and provide relief from high temperatures. For instance, some placed porous water jugs in their windows, where the water would capture the heat, allowing cooled air to pass through.
Thus, the idea of air conditioning is quite old. However, it wasn’t until the Industrial Revolution that people began to manipulate the concept mechanically. In 1819, William Warrel and Robert Salmon received a British patent for their “evaporative cooler,” designed to cool air generally. In 1840, French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet created an early version of a modern evaporative cooler, initially used as an evaporative condenser for steam engines.
Despite these early efforts, cooling towers did not become truly viable until the early 20th century. American inventors began rapidly patenting various versions of the cooling tower, describing them in diverse ways, such as drip coolers, wet boxes, swamp coolers, and desert coolers.
The first modern cooling towers employed direct cooling with tools like fans, sprayers, nozzles, and troughs. Over time, these were replaced by motorized fans, circulating pumps, and similar apparatus. Today, cooling towers come in a variety of configurations.
How It Works
Cooling towers operate based on the principle of evaporative cooling, utilizing the thermodynamic properties of water to remove excess heat from industrial processes or HVAC systems. The process starts with hot water being pumped from the industrial equipment or air conditioning system into the cooling tower. Inside, the hot water is distributed over a series of fill materials designed to increase the exposed surface area, enhancing the interaction between the water and the air flowing through the tower.
Large fans at the base or top of the cooling tower draw in ambient air, which then comes into direct contact with the water-saturated fill material. A small fraction of the hot water evaporates upon contact, transitioning from a liquid to a vapor state. This phase change requires energy, which is absorbed from the remaining water, significantly lowering its temperature.
The cooled water collects in the bottom basin of the cooling tower and is recirculated back to the industrial process or HVAC system, where it absorbs more heat, continuing the cooling cycle. This recirculation allows for continuous and efficient cooling operation.
To maintain optimal performance and prevent mineral buildup, a portion of the water, known as “blowdown,” is periodically purged and replaced with fresh makeup water. This helps maintain the chemical balance and prevents excessive mineral concentration.
Evaporative cooling in cooling towers is highly effective and energy-efficient, making them a preferred choice for various industrial applications. Their ability to efficiently dissipate heat into the atmosphere or recycle it for reuse makes cooling towers essential components in power plants, manufacturing processes, oil refineries, and large-scale HVAC systems, contributing to energy conservation and environmental sustainability.
Types of Cooling Towers
Cooling towers come in several main types: open loop towers, closed loop towers, counter-flow systems, and cross flow systems. Additional types include HVAC cooling towers, industrial cooling towers, evaporative cooling towers, water cooling towers, and chiller cooling towers.
Open loop towers, also known as open circuit cooling towers, distribute water internally where it directly encounters cooling air. The air absorbs heat from the water and exits into the atmosphere, while the cooled water falls into a collection basin.
Closed loop tower systems prevent contact between the cooling agent and the liquid being cooled, allowing the liquid to be recirculated without contamination. This design means the coolant and the material being cooled don’t need to be compatible since they never come into contact.
Counter-flow tower systems operate with opposing air and water flows. Air moves upward, absorbing heat from the water as it flows downward.
Cross flow cooling towers function with perpendicular air and water flows, where air flows sideways and water flows downward.
HVAC cooling towers are typically found in large buildings, used to maintain comfortable interior temperatures.
Industrial cooling towers are more durable than HVAC units because they operate year-round and cool much larger volumes of liquid.
Evaporative and water cooling towers rely on evaporation to release heat into the atmosphere and require a local water source for efficiency, such as rivers, wells, seas, or lakes.
Chiller cooling towers include refrigerant components to cool fluid to even lower temperatures.
Equipment Components
Cooling towers generally comprise several key components, including a wet deck, air inlet and outlet ports, intake louvers, a cool water basin, a fill space, mechanical instrumentation, fans, drift eliminators, and a shell.
Wet decks, also called water distribution decks, feature a set of nozzles that spray water onto fill material to enhance heat transfer.
Air inlet and outlet ports serve as the entry and exit points for air within the tower.
Intake louvers help equalize the air flowing into the fill and retain water within the tower.
Cool water basins, located at the base of the tower, collect the cooled water after it has been discharged.
Fill space, made from PP or PVC in a corrugated or honeycomb pattern, is the main area where cool air extracts heat from hot water.
Mechanical instrumentation includes components such as driveshafts, gearboxes, fans, sensors, pumps, connectors, and cables, which ensure the system operates properly and efficiently.
Fans are crucial for cooling towers that lack a natural draft system. They not only enhance cooling but also help prevent the growth of bacteria, mildew, or mold by providing a level of drying. Fans can be axial or centrifugal and may be positioned overhead, within, or below the system.
Drift eliminators increase the efficiency and environmental friendliness of cooling towers by capturing water droplets in the air stream before they can escape as vapor.
Shells, or cases, enclose the system, holding the liquid until it recirculates. Made from materials such as galvanized steel, ceramic, chemically treated wood, reinforced plastic, or aluminum, shells also provide structural support for the tower’s internal components and fan system.
Benefits
Cooling towers provide numerous critical benefits, making them essential in various industrial processes and climate control systems. One of their main advantages is efficient heat dissipation, which prevents equipment overheating and ensures smooth and reliable operations in power plants, manufacturing facilities, and refineries. By effectively removing excess heat, cooling towers help maintain optimal temperatures, extending equipment lifespan and reducing the risk of costly breakdowns.
In commercial and industrial buildings, cooling towers play a crucial role in HVAC systems, contributing to comfortable indoor environments for occupants. They efficiently remove heat from air conditioning units, allowing the systems to provide pleasant temperatures and improve indoor air quality, which enhances productivity and well-being in work environments.
Another significant benefit of cooling towers is their energy efficiency. Utilizing the principles of evaporative cooling, they consume considerably less energy compared to traditional air-cooled systems. The evaporation process requires relatively low energy inputs, leading to cost savings and a reduced environmental impact, especially in energy-intensive industries.
Cooling towers also promote water conservation. By recirculating cooled water, they minimize overall water usage, which is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity. This recycling process not only reduces water consumption but also decreases the discharge of heated water into natural water bodies, mitigating thermal pollution and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Furthermore, cooling towers contribute to sustainable practices by helping reduce carbon emissions. As energy-efficient cooling solutions, they assist industries in lowering their carbon footprint and moving towards more environmentally friendly operations.
In summary, the benefits of cooling towers include improved equipment performance, energy efficiency, water conservation, reduced environmental impact, and support for sustainable practices. These advantages highlight the indispensability of cooling towers in modern industrial processes, power generation, and climate control systems, playing a vital role in addressing the challenges of a rapidly evolving and environmentally conscious world.
Design and Customization
When designing cooling towers, manufacturers consider several crucial factors, including available space, water sources, electrical supply, materials, and structural capacity. Budget is also a key consideration, as the design of a cooling tower significantly impacts its cost and operational efficiency.
Suppliers can provide either standard or custom cooling towers based on your specifications. Custom cooling towers are ideal for meeting specific volume requirements and adapting to the environment in which they will be used. For instance, manufacturers often create custom cooling towers to address challenges such as piping, electrical sources, and capacity that could affect performance.
To ensure cooling towers fit your application, manufacturers offer a variety of materials and sizes. Cooling towers can be constructed using reinforced glass like fiberglass, stainless steel, ceramic, plastic, and aluminum. Fiberglass is particularly suitable for outdoor applications due to its durability in harsh weather, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. Cooling towers can range in size from small rooftop units to structures as large as 400 feet. In moist, high-temperature environments, manufacturers will incorporate fans into the design. Fans are crucial in these settings as they reduce the likelihood of microorganism growth by circulating water and air throughout the system.
Safety and Compliance Standards
The highest quality assurance for your cooling tower comes from its certification or approval according to the standards of key organizations. Two prominent ones are ASME (The American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and CTI (Cooling Technology Institute). Both associations provide standards and guidelines for the performance and safety testing of cooling towers. Additionally, in the United States, cooling towers must comply with EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) regulations. Under the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990, the EPA enforces rules aimed at reducing emissions from industrial cooling towers.
Beyond certifications and recommendations from ASME, CTI, and the EPA, your cooling tower should also adhere to the standard requirements of your specific industry, whether those are FDA standards, Mil-Specs, or others. If your cooling tower uses combustible materials or poses any fire risk, it must meet the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) 214 standards.
Regularly checking your cooling tower for performance, efficiency, and general safety is crucial. For example, if your system uses evaporative cooling, both ASME and CTI recommend measuring your tower’s effectiveness using wet bulb temperatures. The wet bulb temperature is the lowest temperature to which water in your system can be cooled, measured with a psychrometer. By measuring the wet bulb temperature of air entering the intake port, you can assess your system’s efficiency and calculate the rate of heat transfer through water evaporation. Detailed guidelines for performing these measurements are available from ASME and CTI.
How to Select a Cooling Tower Supplier Using IQSDirectory.com
Selecting the right cooling tower supplier is a critical decision for industries that rely on efficient heat management systems, such as power generation, manufacturing, HVAC, and food processing. Cooling towers are essential for dissipating waste heat, ensuring equipment longevity, and maintaining operational efficiency. IQSDirectory.com, a comprehensive online resource for industrial manufacturers and suppliers, simplifies the process of finding a reliable cooling tower supplier by connecting buyers with top vendors across the United States and Canada. This guide outlines the steps to use IQSDirectory.com effectively to choose a cooling tower supplier that meets your specific needs.
Step 1: Understand Your Cooling Tower Requirements
Before diving into IQSDirectory.com, it’s essential to define your cooling tower needs based on your industry and application. Cooling towers vary in type, size, and specifications, so clarity on your requirements will help you narrow down suppliers. Consider the following:
-
-
- Application: Are you using the cooling tower for power generation, HVAC (e.g., for a data center or hospital), industrial manufacturing (e.g., chemical processing), or food and beverage production? Each application has unique demands, such as hygiene standards for food processing or high heat loads for power plants.
- Type of Cooling Tower: Determine whether you need an open-circuit, closed-circuit, or hybrid cooling tower. For example, closed-circuit towers are better for water conservation, while open-circuit towers are more cost-effective for large-scale heat rejection.
- Heat Load and Capacity: Calculate the heat load (in tons or BTUs) your system needs to reject. This will dictate the size and capacity of the cooling tower.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider factors like local climate, water quality, and space constraints. For instance, in humid regions, you might need a tower with enhanced evaporation efficiency, while in water-scarce areas, a dry or hybrid tower may be preferable.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the cooling tower meets industry standards, such as ASHRAE guidelines for energy efficiency or local regulations for water usage and Legionella prevention.
-
Having a clear understanding of your needs will make your search on IQSDirectory.com more targeted and efficient.
Step 2: Navigate to the Cooling Tower Category on IQSDirectory.com
IQSDirectory.com offers a user-friendly platform to search for industrial suppliers. To find cooling tower suppliers:
-
-
- Visit the Website: Go to IQSDirectory.com.
- Search for Cooling Towers: Use the search bar at the top of the page and enter specific terms like “cooling tower manufacturers,” “HVAC cooling towers,” “industrial cooling towers,” or “water cooling towers,” depending on your needs. Alternatively, browse the categories under industrial equipment to locate cooling tower suppliers.
- Refine by Location (Optional): IQSDirectory.com allows you to search within specific regions, such as states (e.g., Texas, Indiana, or Colorado) or provinces in Canada (e.g., Ontario). This is useful if you prefer a local supplier for faster delivery and support. For example, the platform lists top cooling tower manufacturers in states like Michigan, Illinois, and California, making it easy to find regional vendors.
-
The platform will display a list of premium manufacturers and suppliers, often sorted by state if you’ve applied a geographic filter. Related product categories, such as “Cooling Tower Systems” or “HVAC Cooling Towers,” may also appear at the top of the results page for broader exploration.
Step 3: Explore Supplier Profiles and Previews
IQSDirectory.com provides detailed information about each supplier to help you make an informed decision. Here’s how to use the platform’s features:
-
-
- Preview Supplier Websites: Mouse over a company name in the search results to see a preview of their website on the right side of the screen. This patented feature (part of IQS Directory’s technology) allows you to quickly assess the supplier’s offerings without leaving the page.
- View Company Profiles: Click “View Company Profile” for a deeper dive into a supplier’s details. Profiles include:
- Contact information (phone, email, website).
- Exact geographic location.
- A description of the company’s products and services.
- Product videos, customer reviews, and relevant articles or press releases.
- Assess Product Range: Look for suppliers offering a variety of cooling towers, including new, used, and refurbished units. For example, some suppliers on IQSDirectory.com specialize in reliable thermal transfer systems from top brands, while others offer affordable used towers, which can be cost-effective for smaller operations.
-
This step helps you shortlist suppliers that align with your needs, such as those offering cooling towers for specific applications (e.g., HVAC or industrial processes) or those with a strong presence in your region.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
A supplier’s experience and industry knowledge are critical indicators of their reliability. IQSDirectory.com makes it easy to assess this through company profiles and customer feedback:
-
-
- Check Industry Focus: Look for suppliers with experience in your sector. For instance, a supplier listed under “HVAC Cooling Towers” will likely have expertise in supporting commercial buildings, while one under “Industrial Cooling Towers” may specialize in manufacturing or power generation applications.
- Review Customer Feedback: Company profiles on IQSDirectory.com include customer reviews, which provide insights into the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and service. Positive reviews from businesses in your industry are a good sign.
- Look for Detailed Descriptions: Suppliers with comprehensive profiles often highlight their expertise, such as years in business, types of cooling towers they manufacture (e.g., open-circuit, closed-circuit), and specific solutions they offer (e.g., reducing downtime or maintenance costs).
-
Suppliers on IQSDirectory.com are noted for helping companies save time and money, often by offering solutions that reduce maintenance costs and downtime. Choose a supplier with a proven track record in delivering these benefits.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Options
IQSDirectory.com streamlines the process of contacting suppliers and gathering quotes, allowing you to compare options efficiently:
-
-
- Submit a Request for Quote (RFQ): Click “Request a Quote” on a supplier’s profile to submit an RFQ. IQS Directory’s patented RFQ tool allows you to contact multiple suppliers with a single form, saving time. Provide details about your cooling tower requirements, such as capacity, type, and application, to receive accurate quotes.
- Compare Pricing and Services: Once you receive responses, compare the quotes based on pricing, delivery timelines, and additional services (e.g., installation support, maintenance plans). Some suppliers on IQSDirectory.com offer competitive pricing for new, used, and refurbished units, making it easier to find cost-effective options.
- Assess Value-Added Services: Look for suppliers who provide extras like on-site surveys, custom tower design, or water treatment solutions to prevent issues like scaling or Legionella growth. These services can enhance the long-term performance of your cooling tower.
-
This step ensures you find a supplier that offers the best value, balancing cost with quality and support.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Reputation and Support
A supplier’s reputation and after-sales support are crucial for a successful partnership. IQSDirectory.com provides tools to evaluate these factors:
-
-
- Check Company Profiles for Updates: IQS Directory and the listed companies periodically review profile information to ensure accuracy. Look for suppliers with up-to-date profiles, as this indicates they are actively engaged with the platform and their customers.
- Explore the IQS Newsroom: Access the IQS Newsroom (linked at the top of every page) to find current news on listed companies, industry initiatives, and upcoming events. This can provide insights into a supplier’s reputation, innovation, and involvement in the industry.
- Contact Suppliers Directly: Use the contact details in the company profile to reach out via email or phone. Ask about their experience with projects similar to yours, their approach to customer service, and their ability to provide ongoing support.
-
Suppliers on IQSDirectory.com are often highlighted for their ability to save maintenance costs and reduce downtime, so prioritize those with a strong reputation for reliability and support.
Step 7: Consider Geographic Proximity and Delivery Speed
While not always a primary factor, the supplier’s location can impact delivery times and service availability. IQSDirectory.com allows you to filter suppliers by state or province, which can be advantageous:
-
-
- Local Suppliers: Choosing a supplier in your region (e.g., Texas, Indiana, or Ontario) can lead to faster delivery and easier access to on-site support. For example, IQSDirectory.com lists top cooling tower manufacturers in various states, making it easy to find local options.
- Delivery Timelines: Ask suppliers about their lead times, especially if you need a cooling tower urgently. Some suppliers on IQSDirectory.com are noted for offering quick delivery, which is critical for minimizing downtime.
-
Geographic proximity can also reduce shipping costs and facilitate better communication with the supplier.
Additional Tips for Using IQSDirectory.com
-
-
- Leverage Related Categories: If you don’t find the exact cooling tower supplier you need, explore related categories like “Cooling Tower Systems” or “Water Cooling Towers” for more options.
- Share and Connect: IQSDirectory.com allows you to share company profiles on social media or find related manufacturers, helping you expand your search if needed.
- Provide Feedback: IQS Directory values user feedback to improve its services. If you have suggestions or need additional information, use the “Contact” link at the top of the page to reach out.
-
Why Use IQSDirectory.com to Find a Cooling Tower Supplier?
IQSDirectory.com offers several advantages over general search engines:
-
-
- Targeted Search Results: The platform provides highly relevant results tailored to the industrial sector, unlike broader search engines like Google.
- Comprehensive Profiles: Detailed company profiles, customer reviews, and product videos help you make informed decisions quickly.
- Patented Features: Tools like website previews and the RFQ system streamline the supplier selection process.
- Geographic Filtering: Search by state or province to find local suppliers, ensuring faster delivery and support.
-
What is a cooling tower and how does it work?
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device that removes heat from water or other fluids using the principle of evaporative cooling. Hot water from industrial processes or HVAC systems is circulated through the tower, where it is distributed over fill material and exposed to air. As some of the hot water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the remaining water, lowering its temperature, and the cooled water is recirculated back into the system.
Which industries commonly use cooling towers?
Cooling towers are used in power generation, industrial manufacturing (such as steel, chemical, and petrochemical), HVAC systems in commercial and residential buildings, food and beverage processing, oil and gas, pharmaceutical manufacturing, pulp and paper production, and plastic and rubber manufacturing. These industries rely on cooling towers to manage heat and maintain efficient operations.
What are the main types of cooling towers?
The main types of cooling towers include open-loop (open circuit) towers, closed-loop (closed circuit) towers, counter-flow systems, and cross-flow systems. Other varieties include HVAC cooling towers, industrial cooling towers, evaporative cooling towers, water cooling towers, and chiller cooling towers, with each type suited to specific applications and operational requirements.
What are the key components of a cooling tower?
Key components of a cooling tower include a wet deck (water distribution system), air inlet and outlet ports, intake louvers, cool water basin, fill space, mechanical instrumentation (such as fans, driveshafts, sensors, and pumps), drift eliminators, and the shell or case that encloses the system and supports internal structures.
What are the main benefits of using a cooling tower?
Cooling towers offer several benefits, including efficient heat dissipation, prevention of equipment overheating, enhanced energy efficiency, water conservation through recirculation, reduced environmental impact, and support for sustainable industrial practices.
What factors should be considered when selecting or using a cooling tower?
When selecting or using a cooling tower, it is important to consider water quality, environmental impact, noise levels, space requirements, material selection, heat load, and regulatory compliance. Regular maintenance and water treatment are also essential to prevent scaling, corrosion, and microbial growth.
Which certifications and standards apply to cooling towers?
Cooling towers should comply with ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and CTI (Cooling Technology Institute) standards, as well as EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) regulations in the United States. Industry-specific standards such as FDA, Mil-Specs, and NFPA 214 may also apply based on application and material used.





 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers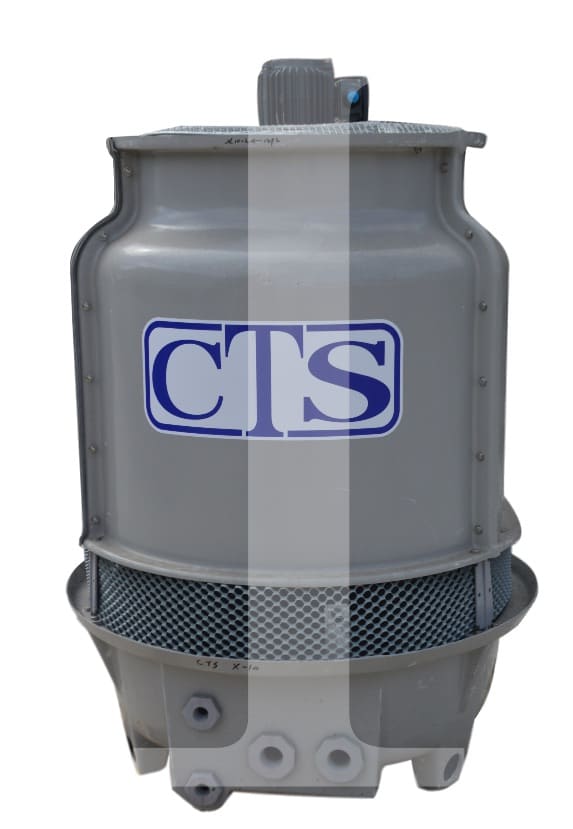 Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services