Facilities such as power plants, oil refineries, petrochemical and natural gas processing plants all use evaporating and water cooling to remove heat.
Specific applications of water cooling towers include air conditioning towers and HVAC cooling towers, as well as water treatment. Water is an ideal substance to use for industrial cooling as it has a high specific heat capacity and greater thermal conductivity than many other liquids. Furthermore, when water is released into the atmosphere through the process of evaporation, it is able to be absorbed into the water cycle again.
It is a naturally available resource although sources of cooling water vary according to the location of the cooling tower system and the natural provision. These sources may include rivers, seas, wells or lakes. Water cooling towers use evaporation of the source water to cool and can also be classified as “wet” cooling towers. Some applications require higher quality water and therefore purified water can be used instead of natural water, although it is likely to be much more expensive and only used for specific industries such as biochemical or food processing.
The coolant water is pumped into the cooling tower system and it is circulated through heat exchangers. The heat exchangers are heated by the industrial processes of the plant and the energy given off there, and can be heated water or another liquid, or hot air. The waste heat is absorbed by some of the coolant water to the point of evaporation at which it is released as warm moist air. Evaporation causes the air to leave the surface of the water and as a result the heat exchangers cool.
The warm air is less dense and it rises into the atmosphere. Water is moved around the heat exchangers continuously in order to keep the cycle of heat removal and evaporation moving. The cycle of cool water combined with the evaporative process results in some water loss and therefore water needs to be brought in from the water source to replace it with fresh cool water. Thermal pollution is a concern if precautions are not taken to prevent heated water being returned to the natural source and disturbing the ecology of the river or lake.
Another consideration to have in regard to the location of the tower when using water cooling is the temperatures the tower is to experience in the natural environment. If the temperatures are likely to drop during winter months, precautions should be taken to prevent freezing damage to piping and interior surfaces.



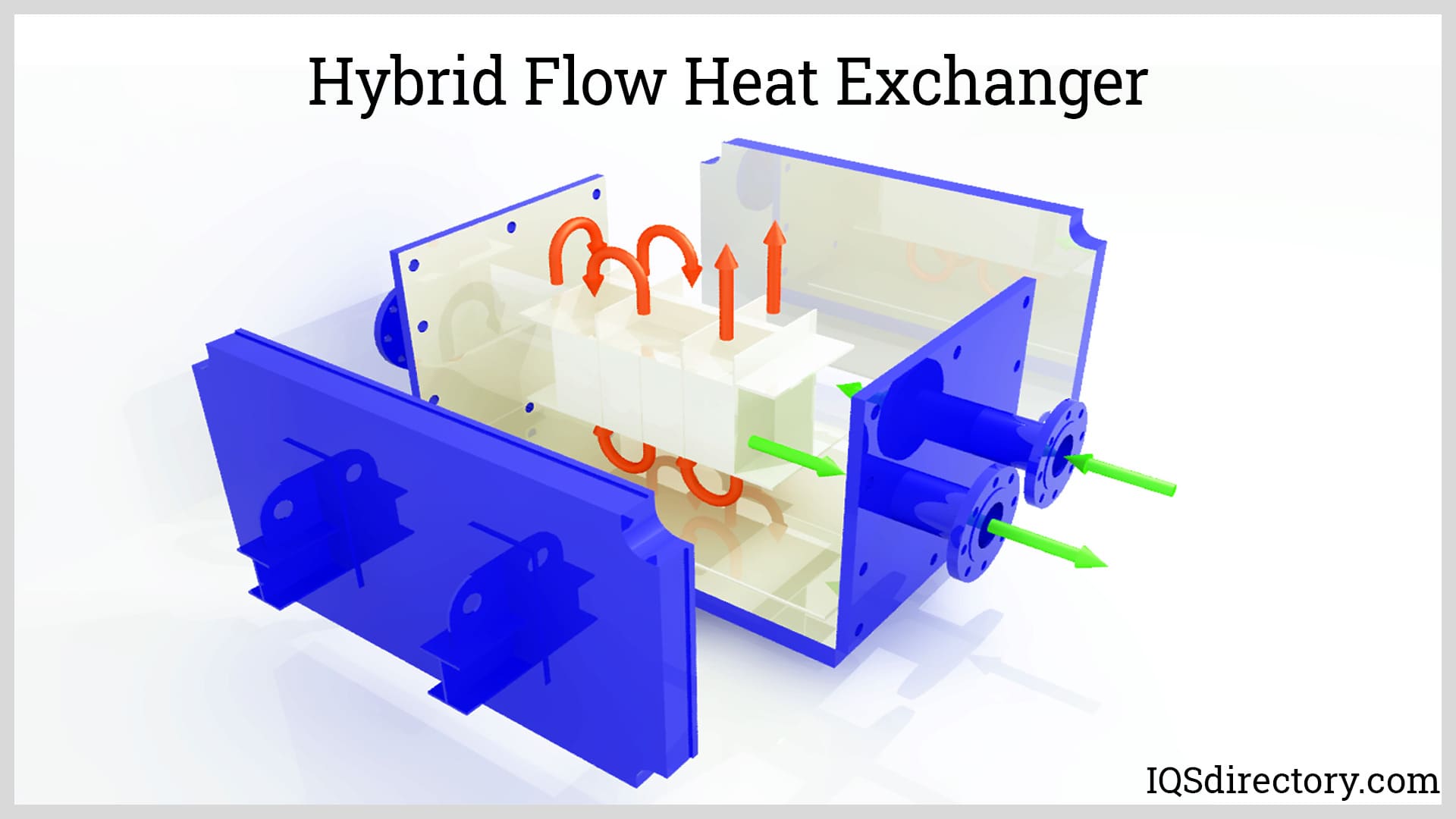

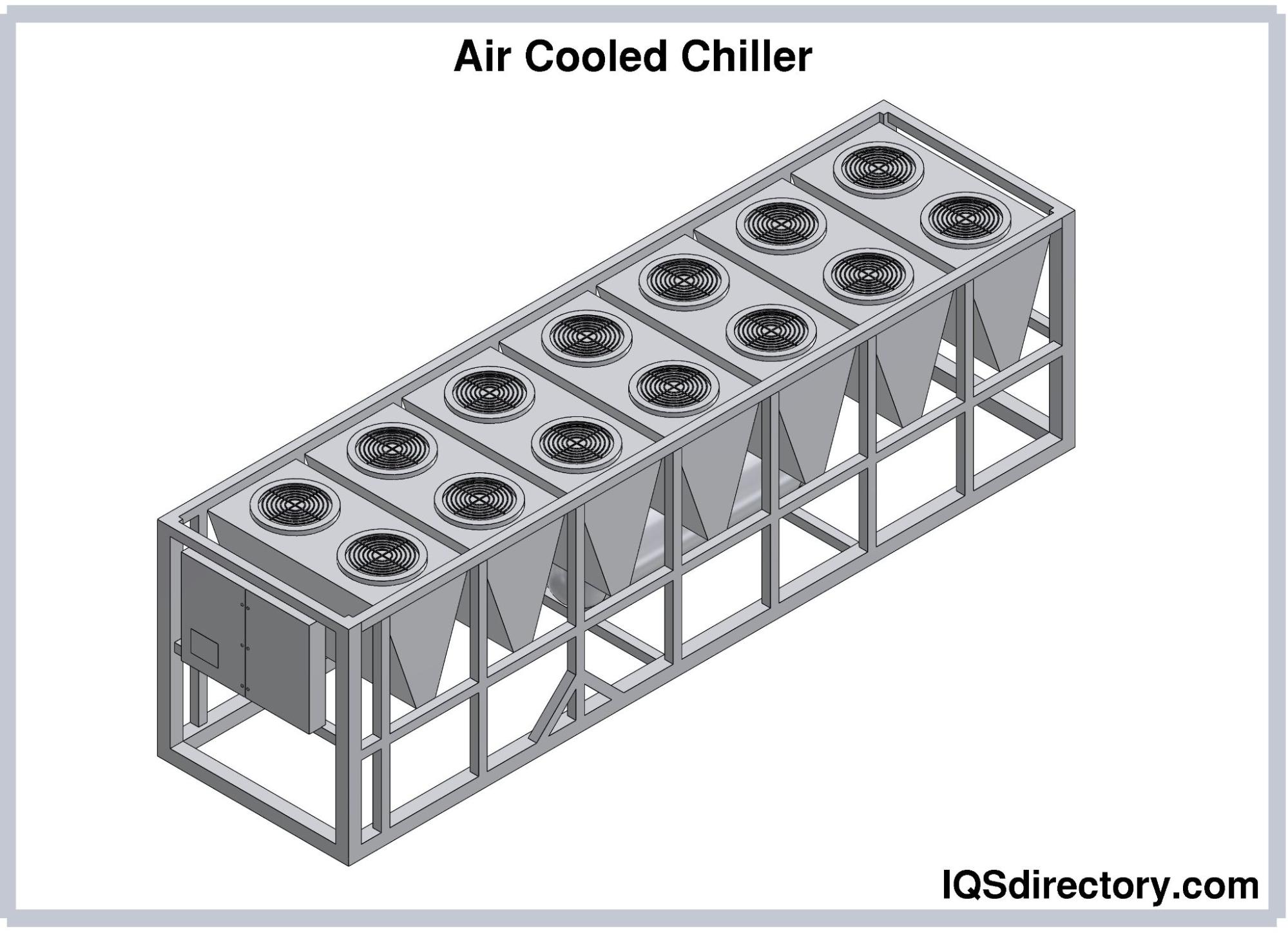
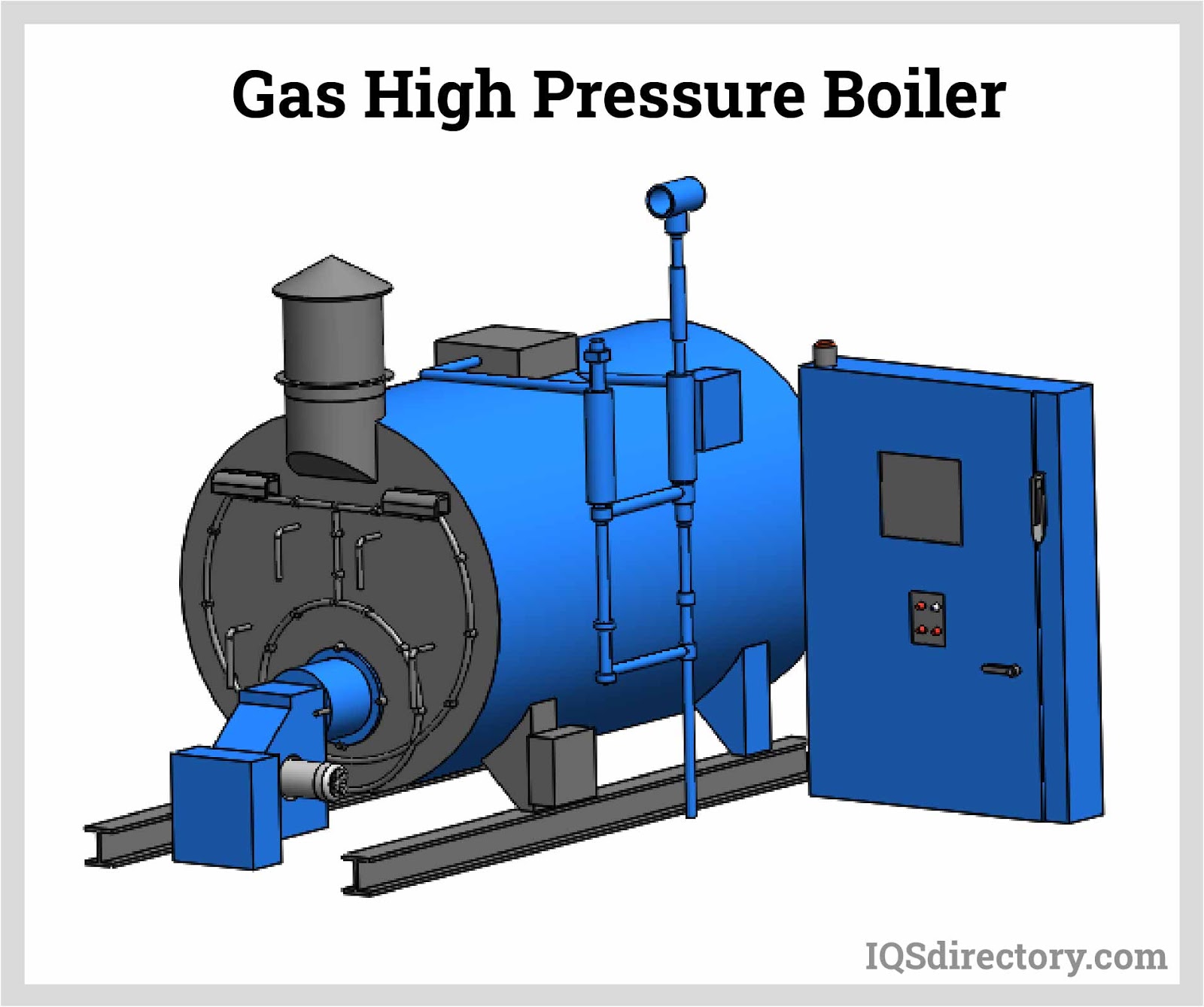
 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services